Precalculus: Operations on polynomials
1. Division of polynomials
We want to divide two polynomials: P(x) and Q(x)
Degree(P(x)) > Degree(Q(x))
1. Without remainder:
Let two polynomials:
P(x) = x3 + 2 x2 + 3x - 6, and
Q(x) = x - 1
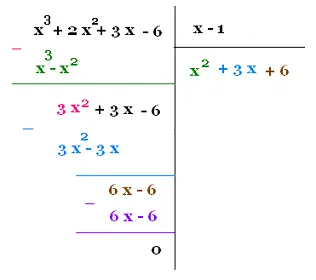
x3 + 2 x2 + 3x - 6 = (x2 + 3 x + 6)(x - 1)
2. With remainder:
P(x) = x3 + 2 x2 + 3x, and
Q(x) = x - 1
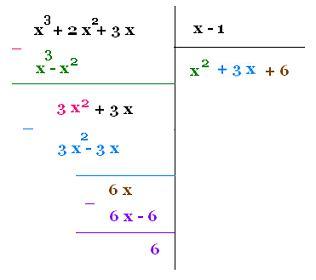
x3 + 2 x2 + 3x = (x2 + 3 x + 6)(x - 1) + 6
2. Rational Functions
We are interested to evaluate integrals
of rational functions: R(x) = P(x)/Q(x)
Degree of P(x) > degree of Q(x).
Dividing P(x) by Q(x) gives:
P(x)/ Q(x) = A(x) + B(x)(x)/Q(x)
B(x) is the remainder, and
degree of B(x) < degree of Q(x).
Now, we focus on the technique to decompose
P(x)/Q(x) when the degree of P(x) is < degree of Q(x).
1. The technique of partial
fraction decomposition:
Case1:
If
Q(x) = (a1 x + b1)(a2 x + b2)(a3 x + b3) ... (an x + bn)
Then:
P(x)/Q(x) = A1/ (a1 x + b ) + A2/ (a2 x + b2) +
A3/ (a3 x + b3) + ... + An/ (an x + bn)
Case2:
If
Q(x) = (a x + b)n
Then:
P(x)/Q(x) = A1/ (a x + b)1 + A2/ (a x + b)2 +
A3/ (a x + b)3 +... + An/ (a x + b)n
Case3:
If
Q(x) = (a1 x2 + b1x + c1)(a2 x2 +
b2x + c2)(a3 x2 + b3x +
c3) ... (an x2 +
bnx +cn)
Then:
P(x)/Q(x) = (A1x + B1)/ (a1 x2 +
b1x + c1) + (A2 x + B2)/ (a2 x2 + b2x + c2) +
(A3x + B3)/ (a3 x2 + b3x + c3) + ...+ (n x + Bn)/ (an x2 + bnx + cn)
Case4:
If
Q(x) = (a x2 + bx + c)n
Then:
P(x)/Q(x) = (A1x + B1)/ (a x2 + bx + c)1 + (A2 x + B2)/ (a x2 + bx + c)2 +
(A3 x + B3)/ (a x2 + bx + c)3 +... + (An x + Bn)/ (a x2 + bx + c)n
Examples:
Example 1:
R(x) = 4x - 3 /(x - 1)(x + 3)2
R(x) = a/(x - 1) + b/(x + 3) + c/(x + 3)2
Example 2:
R(x) = (4x2 + 1)/(x2 + 2)(x - 1)2(x)3
= (a x + b)/(x2 + 2) + c/(x - 1) + d/(x - 1)2 + e/x + f/x2 + g/x3
2. Finding constants:
Example:
R(x) = P(x)/Q(x) = (x - 1 )/(x - 2)(x - 3) = a/(x - 2) + b/(x - 3).
Equating the numerators of P(x) and the one
of the decomposed fraction, yields a formed
equation:
x - 1 = a(x - 3) + b(x - 2)
We have two ways:
1. Substituting the singular points in the
formed equation,
2. Equating the coefficients of each degree of
the formed equation.
1.
Singular points: 2 and 3
With 2, we have: 2 - 1 = a(2 - 3) + b(2 - 2) then
a = -1
With 3, we have: 3 - 1 = a(3 - 3) + b(3 - 2) then
b = 2
2.
The formed equation
x - 1 = a(x - 3) + b(x - 2)
Developing gives:
x - 1 = ax - 3a - 3a + bx - 2b = (a + b)x -3a - 2b, so
1 = a + b, and
-1 = -3a - 2b
Substituting the first in the second yields:
- 1 = - 3(1-b) - 2b = -3 + b, then: b = 2 and a = -1
We write:
(x - 1 )/(x - 2)(x - 3) = -1/(x - 2) + 2/(x - 3)
Therefore, the integral becomes easy to evaluate:
∫ dx (x - 1 )/(x - 2)(x - 3) = -1 ∫ dx /(x - 2) + 2∫ dx /(x - 3) =
- ln(x -2) + 2 ln(x - 3) + constant.
4. Exercices
a) Give the partial fraction decomposition of
the following, and find the related constants:
16/(x - 3)(x + 5)
(2 x - 1)/(x2 - 7x + 10)
(5x - 3)/(x - 2)(x + 5)2
b) Give the partial fraction decomposition of
the following:
(x + 1)/(x - 1)(x2 + x + 1)
14/(x2 + x + 1)2
(2x - 1)/(x2 + 1)3
(2x2 - 1)/(x + 3)2(x2 + 1)3
Solutions
|