Nuclear Physics
The nucleus
Radioactivity
Applications
Particle accelerators
© The scientific sentence. 2010
| γ-decay
1. Definition
The nucleus in an atom can be found in an excited
state or ground state. The involved energy of excitation
is of the order of 1 MeV, compared to a few eV for atomic
energy level. It is due to the great strength of nuclear
interactions.
When a nucleus is placed in an excited state (by
bombardment with high energy particle or by radioactive
transformation), it can decay to the ground state by
emitting one or more photons called gamma rays photons
, with typical enrgies of 10 keV to 5 MeV.
This process is called γ-decay.
2. Example:
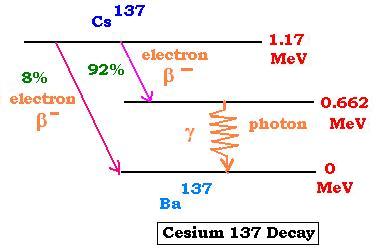 The nuclide Cesium137 undergoes two β minus
decays. The most probable is the one that leads to the
excited (metastable) *Cesium137, which emits a photon
(γ-decay) 0.662 MeV of energy before being transformed
into a stable nuclide Ba137 at the ground state.
The Cesium-137 (137,55) has a half-life of about 30 years.
Its activity is about of 3.20 x 10 12 Bq per gram.
The nuclide Cesium137 is used to calibrate
radiation-detection equipments. The emitted photons of 0.662
MeV energy can be useful in food irradiation and in the
radio-oncology (radiotherapy of cancer).
The nuclide Cesium137 undergoes two β minus
decays. The most probable is the one that leads to the
excited (metastable) *Cesium137, which emits a photon
(γ-decay) 0.662 MeV of energy before being transformed
into a stable nuclide Ba137 at the ground state.
The Cesium-137 (137,55) has a half-life of about 30 years.
Its activity is about of 3.20 x 10 12 Bq per gram.
The nuclide Cesium137 is used to calibrate
radiation-detection equipments. The emitted photons of 0.662
MeV energy can be useful in food irradiation and in the
radio-oncology (radiotherapy of cancer).
|
|