Mathématiques 45: Algèbre vectorielle
Produit vectoriel
1. Produit vectoriel: Le Cas simple
Deux vecteurs
et
supportés par les axes.
\[\vec{\mathbf{V}_1} \times \vec{\mathbf{V}_2} = \begin{vmatrix}
\mathbf{i} & \mathbf{j} & \mathbf{k} \\
x1 & y1 & 0 \\
x2 & y2 & 0
\end{vmatrix} =
\begin{bmatrix}
0 \\
0 \\
x_1 y_2 - y_1 x_2
\end{bmatrix} \]
2. Produit vectoriel: Cas général
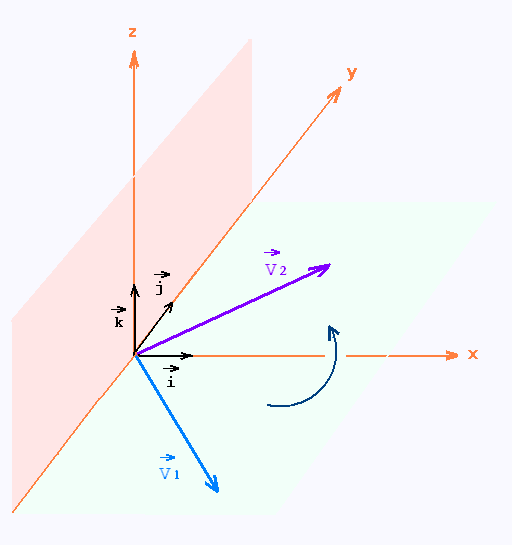
\[\vec{\mathbf{V}_1} \times \vec{\mathbf{V}_2} = \begin{vmatrix}
\mathbf{i} & \mathbf{j} & \mathbf{k} \\
x_1 & y_1 & z_1 \\
x_2 & y_2 & z_2
\end{vmatrix} =
\begin{bmatrix}
y_1 z_2 - y_2 z_1 \\
x_2 z_1 - x_1 z_2\\
x_1 y_2 - y_1 x_2
\end{bmatrix} \]
3. Propriétés du produit vectoriel
Le produit vectoriel n´est pas commutatif,
il
est alterné:
Distributivité par rapport à l´addition:
Produit par un scalaire:
Le produit vectoriel de deux vecteurs
liés (ou colinéaires ou parallèles) est nul.
↔
//
4. Interprétation géométrique
du produit vectoriel
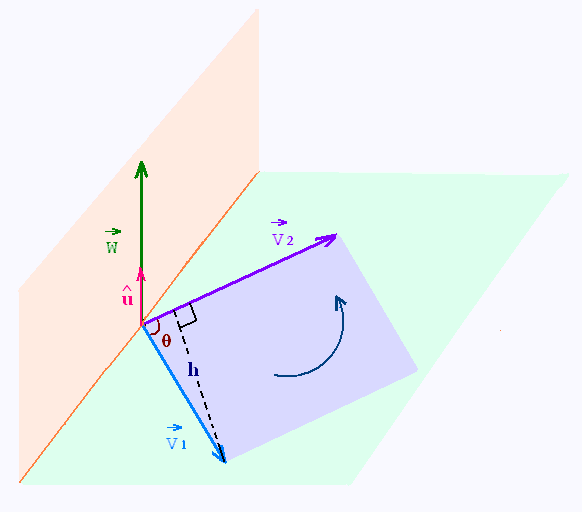
La définition du produit vetoriel s'ecrit:
|