Calculus I
Limits
Derivative
Exercices
Applications
Marginal analysis
© The scientific sentence. 2010
|
Calculus I: Symmetry and graph
1. Parity of a function
A function f is even if for all x in its domain,
f(- x) = f(x)
A function f is odd if for all x in its domain,
f(- x)= - f(x)
Examples:
a) f(x) = x2 + 4 is even because f(- x) = (- x)2 + 4 =
x2 + 4
b)f(x) = sin x is odd because sin(- x) = - sin (x)
c) f(x) = 2x + 3 is neither even nor odd.
2. Symmetry
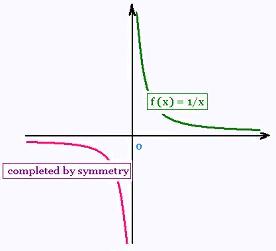
The graph of an even function is symmetrical with respect to the axis
y while the graph of an odd function is symmetric
with respect to the origin.
When a function is odd or even, we study the function in its
interval of symmetry and complete by symmetry.
Example:
f(x) = 1/x is odd. Its interval os symetry is I = [0, + ∞[.
We study and graph this function on I and complete by symmetry
with respect to the origin.
3. Exercices
|
|